[Research] Teppei Kitahara’s paper was highlighted as one of the Editors’ Suggestions of Physical Review Letters
Novel mechanism to avoid theoretical bound on kaon rare decays
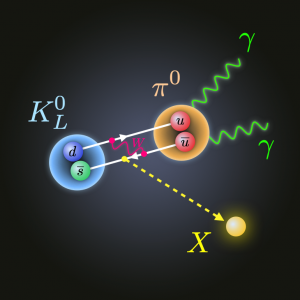
Researchers try to revisit a theoretical bound, which is based on symmetries, between the charged and neutral kaon rare decays into the pion and neutrinos. Last September, KOTO experiment searching for neutral kaon rare decay reported events with an unexpected rate, which is much bigger than the standard model predictions. So far, KOTO experiment has not claimed that these events are the rare kaon decay signals. On the other hand, a theoretical upper bound on this rate comes from charged kaon data, and is incompatible with the events if the events are assumed to be the signals. A research collaboration, including Designated Assistant Professor Teppei Kitahara at KMI and Institute for Advanced Research, Nagoya University, has proposed novel mechanisms to avoid the upper bound by introducing a new light long-lived particle. If the KOTO events are confirmed as the signals, the proposed new particle is strongly anticipated. This research was published in Physical Review Letters on February 19, 2020, and selected as Editors’ Suggestion, Featured in Physics (Synopsis), and the cover of Volume 124, Issue 7.
Link
Featured in Physics (Synopsis)
https://physics.aps.org/synopsis-for/10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.071801
Paper Information
Physical Review Letters (February 19, Vol 124, (2020), 071801), “New Physics Implications of Recent Search for at KOTO”
DOI: https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.071801



